fMRI → Network: Theoretical and Technical outline
Preprocessing
The preprocessing steps involve the following: (1) correction for slice-timing differences, (2) correction of head-motion across functional images, (3) coregistration of the anatomical image and the mean functional image, and (4) spatial normalization of all images to a standard stereotaxic space (Montreal Neurological Institute; MNI) with a voxel size of 3 × 3 × 3 mm3.
De-noising
“Furthermore, the BOLD time series in MNI space were subjected to spatial independent component analysis (ICA) for the identification and removal of artifacts related to blood pulsation, head movement and instrumental spikes and those that correlate with the white matter and CSF patterns (Sui et al., 2009; Mantini et al., 2013). The BOLD artifact removal procedure was performed using the GIFT toolbox (http://mialab.mrn.org/software/gift/index.html).” At CAHBIR, we use TEDANA for this.
Clustering/ICA/CCA/PCA etc of the voxels at each timeseries
- Can use a parcellation atlas
- common ones: Yeo, Schaefer
- atlases list: https://www.lead-dbs.org/helpsupport/knowledge-base/atlasesresources/cortical-atlas-parcellations-mni-space/
- ”No global signal regression was performed. For each recording session (subject and run), the BOLD time series from the 998 ROIs of the brain atlas (Hagmann et al., 2008) were averaged over the corresponding 66 brain regions.”
Correlation matrix of the ROIs at each timepoint
- “Finally, we concatenate in time the remaining sessions for each parcel and calculate the correlation matrix (FC).”
- Usually Pearson’s correlation
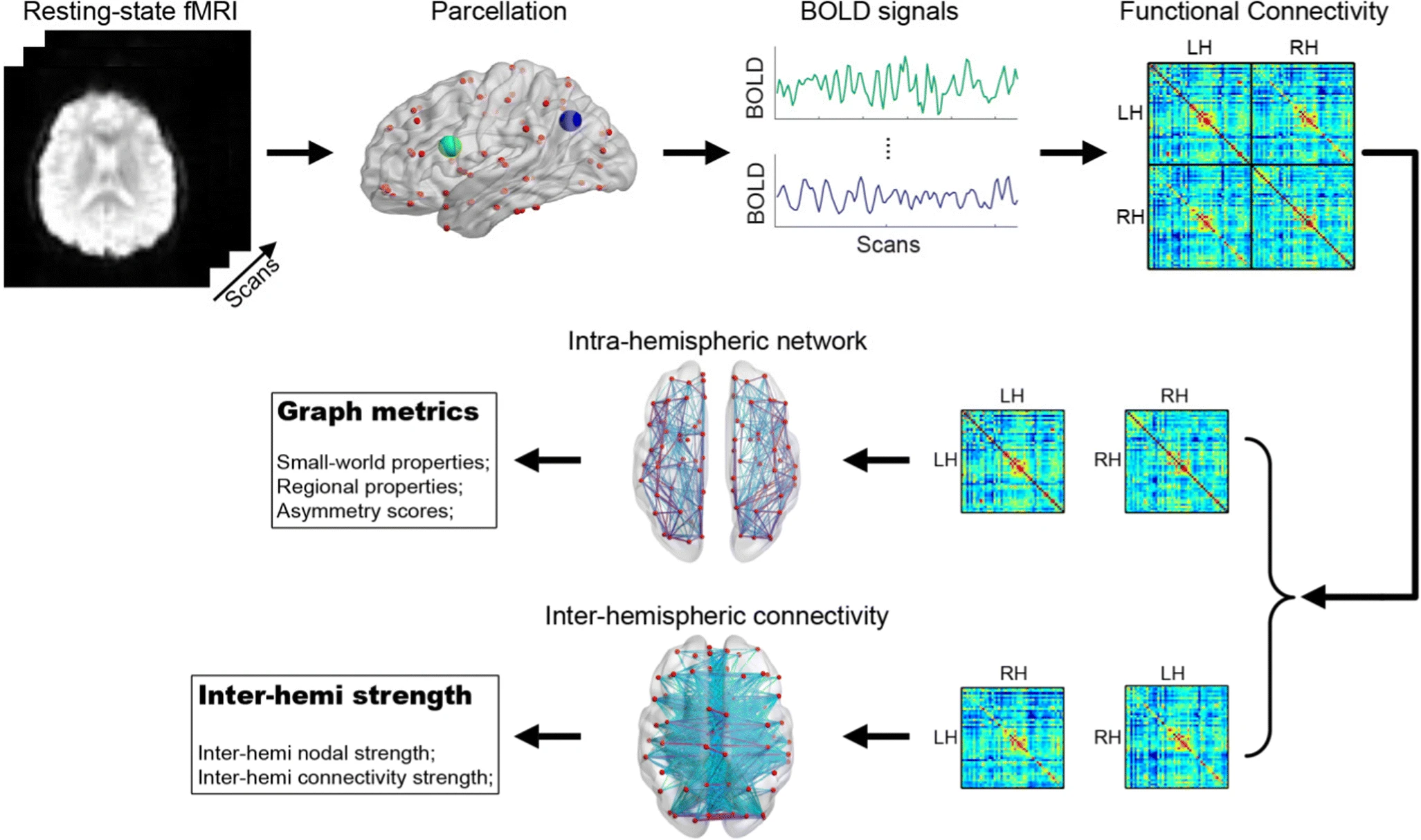
Figure 1: Workflow from fMRI scan to network data, specifically as applied to lateralization metrics
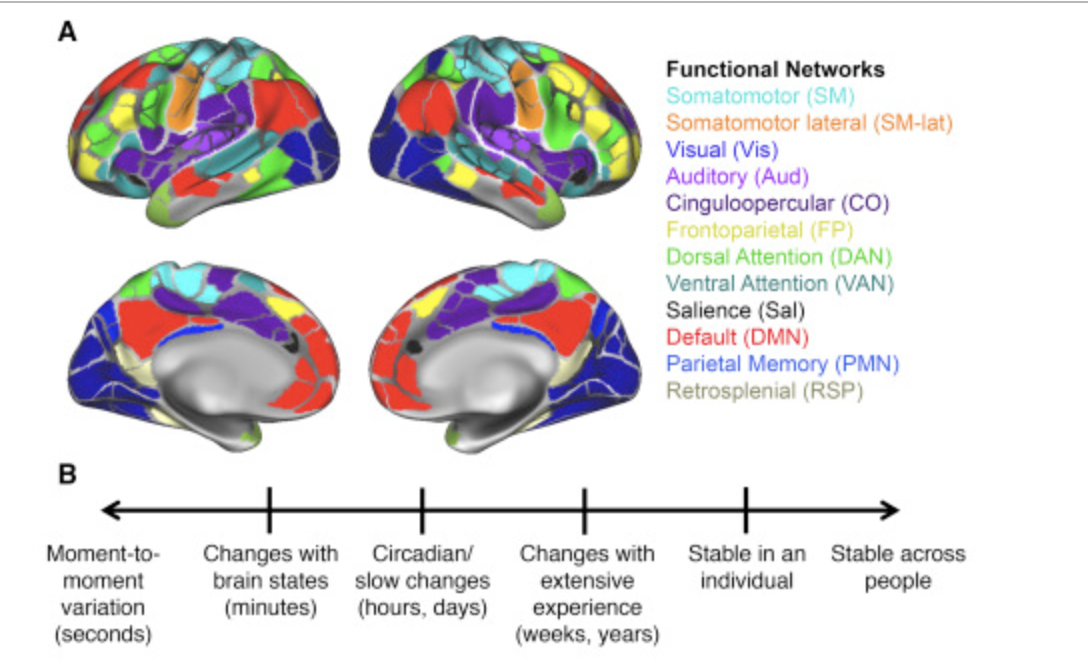
Functional Networks parcellation, a common example of the currently accepted functional networks