FreeSurfer Overview
Date: January 16, 2024 1:15 PM
Table of Contents
**Freesurfer is a neuroimaging software package. More information at https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/
Function of FreeSurfer
- Takes your T1 weighted image from fMRI or MRI → Labelled brain and stats
- will completely label the anatomy of the brain
- output an array of measures of anatomy (5-10hrs of analysis)
- automated— go check for artifacts if it’s relevant to your results
- cortex flattened out
- subcortical organs
- does cortex-surface-based analysis & volumetric analysis
- multi-modal integration
- fMRI (task, rest, retinopy)
- diffusion data
Download and Install FreeSurfer
FreeSurfer 7 Download ← Installation Walk Through
Installation Demo Video for MacOS:
Source: FreeSurfer Download and Install
FreeSurfer Tutorials
Overview
- Introduction to Free Surfer video series
- FreeSurferAnalysisPipelineOverview
- FreeSurferBeginnersGuide
- FreeSurferWorkFlows
- FreeSurferApplications
- FreeSurferCommands
Basics
- Introduction to FreeSurfer Output (slides, video)
- Practice Working with Data
- Troubleshooting FreeSurfer Output (slides, video)
- Group Analysis (slides, video)
- Multiple Comparisons via command-line (Permutation) (slides)
- Qdec Group Analysis via GUI
- ROI Analysis ( slides, video)
- Multimodal Analysis (slides- Part 1, slides- Part 2, video)
Specialized topics:
- Longitudinal Processing, Edits and Post-Processing (slides, video)
- Diffusion Analysis (slides, video)
- TRACULA (slides, video)
- FS-Fast - fMRI Analysis (slides)
Other:
Running Full Anatomical Analysis on FreeSurfer
Running
Open terminal →
recon-all \
-i <one slice in the anatomical dicom series> \
-s <subject id that you make up> \
-sd <directory to put the subject folder in> \
-all
- will take 5-20 hours
“-i file.dcm”
- only need to say 1 file in the set of ~180, it will find automatically the rest
- you can also use .nii files
- add “-i file2.dcm” if you have two series of diff scans you want to run
“bert”
- use whatever name you want it to be, maybe subject ID
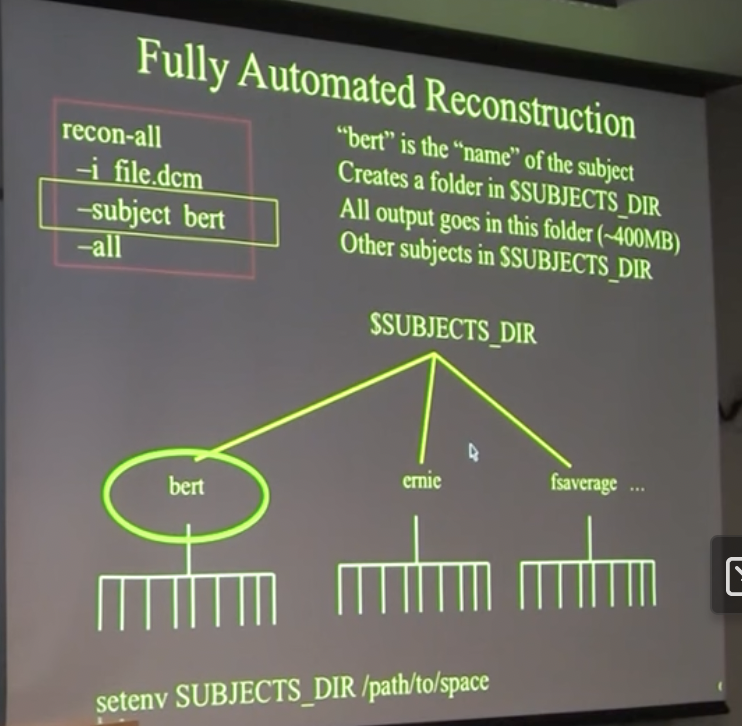
Upon completion…
Will create folder with subfolders:
~400 MB
mri=volume analysis
surf, label =surface analysis
stats = txt files with stats for all the other files in other folders

To check for errors/ debug:
scripts/recon-all.log ← shows all the terminal commands that ran, log
What happens inside this full processing?
All commands: Recon-All Dev Table
- This shows you the command, function and output for each step
Terms
anatomically derived defect
A topological defect in the cortical surface that arises from a feature of normal neuroanatomy to be distinguished from defects arising entirely from segmentation errors. See topological defect
artifact
A feature that appears in an image but is not actually present in the imaged object.
average convexity
The signed distance that a vertex moves during the inflation process.
brain volume
The T1 volume after the skull and other non-brain structures have been removed. This volume can be viewed using tkmedit.
canonical surface
Surface-based atlas constructed from the cortical surfaces of 40 normal individuals (used for inter-subject averaging).
conversion/averaging
Process of converting and averaging multiple structural acquisitions from the native magnet format into the native FreeSurfer format (see COR files).
COR files
The native file format used by FreeSurfer to store 3D structural image data.
Euler number
After Leonhard Euler (1707-83). A topological invariant of a surface that can be computed from the number of edges, vertices and faces in a polygonal tessellation (command mris_euler_number ). The Euler number of a sphere will equal 2; the Euler number of a surface with n handles is 2 2n.
filled volume
The wm volume after separation of the left and right hemispheres and filling of each hemisphere. This volume can be viewed using tkmedit.
flattening
Producing a planar (flat) representation of a patch of the cortical surface that has minimal metric distortion.
gyrus
A fold or convolution of brain tissue (an outward folded region).
hypointensities (wm)
Dark white matter on a T1-weighted image.
hypointensities (non-wm)
Dark gray matter on a T1-weighted image.
inflated surface
The smoothwm surface after inflation. This surface can be viewed using surfer.
inflation
The process of smoothing the cortex while minimizing metric distortion, so that all sulci are fully visible and surface distances are apparent to visual inspection.
intensity
Measured amount of magnetic field at a given spatial location, represented by a voxel (higher SNR signal to noise ratio means voxels will have a higher intensity relative to the background noise, and appear brighter).
label
A particular region of interest. e.g. in tksurfer the label would be a region of interest in the surface. In tkmedit a label is a region of interest in the volume.
morphing
Computer graphics technique whereby a mapping is computed that smoothly transforms one image or surface into another.
morphometrics
The study of geometric properties of the human brain.
motion correction
Processing multiple structural volumes so that the effects of subject movement are minimized. This is typically done by aligning multiple images/volume to an initial image/volume (see conversion/averaging).
MRI volume
The three dimensional volumetric data set collected from a MRI scanner.
orig volume
The original MRI volume. This volume can be viewed using tkmedit.
orig surface
The first surface constructed by covering the labeled voxels in the filled volume. This surface can be viewed using surfer.
pial
Pertaining to the delicate pia mater which envelops the brain (gray matter). Also, the model of the pial surface (?h.pial).
pial surface
The refined estimate of the gray/CSF boundary (pial surface). This surface can be viewed using surfer.
region growing process
An algorithm that groups voxels or sub-regions into larger regions.
RF-field inhomogeneities
Spatial variations in the Radio Frequency (RF) excitation pulse. These variations result in changes in the measured intensity for a given tissue class that are related to the spatial location of the voxel.
segmentation
Labeling of tissue classes from MRI data (e.g. white matter).
smoothing
Process of producing a relatively even and regular cortical surface.
smoothwm surface
The orig surface after smoothing. This surface can be viewed using surfer.
sulcus
A groove or furrow in brain tissue (an inward folded region).
supertessellated icosahedron
Polygonal approximation to a sphere.
T1
Longitudinal relaxation constant.
T1 volume
The MRI volume after intensity normalization. This volume can be viewed using tkmedit.
T1 Weighted Image
A magnetic resonance image where the contrast is predominantly dependent on T1.
T2 Weighted Image
A magnetic resonance image where the contrast is predominantly dependent on T2.
T2
Transverse relaxation constant.
Talairach coordinate
The corresponding location in the Talairach atlas for a given point in a brain that has been coregistered with the atlas (Talairach et al, 1967).
tessellation
Covering of a surface by repeated use of a single shape.
topology
The properties of a surface related to its connectivity that are unaffected by geometric (i.e. rubber sheet) transformations.
topological defect
A portion of a surface that results in the surface topology differing from that of a sphere.
volume
A 3-D data set that typically contains either intensity information derived from the original MRI, or the results of segmenting this data into tissue classes.
voxel
The basic element of an MRI volume (analogous to a pixel in a 2-D image). The volume of a structural voxel is approximately 1 mm3.
white surface
The refined estimate of the gray/white boundary. This surface can be viewed using surfer.
wm volume
The brain volume after white matter segmentation. This is also the volume that is manually edited. This volume can be viewed using tkmedit.