Slurm Jobs Tutorial - Rutgers
Job scheduler (batch system)
The job scheduler used on OARC-managed clusters is SchedMD’s SLURM Workload Manager.
Any memory-intensive or compute-intensive process should be run using scheduled resources and not simply run on one of our shared login nodes. In short, do not run applications on the login nodes.
Basic Slurm Job Example:
- Create a script named
.sh (make sure to add #!/bin/bash at top) - Fill in this with your specs
#! /bin/bash
#SBATCH --partition=p_dz268_1
#SBATCH --job-name=<some job name>.sh
#SBATCH --requeue
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --ntasks=1
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=1
#SBATCH --mem=2000
#SBATCH --time=*48:00:00*
#SBATCH --output=/path/to/folder/<some job name>.out
#SBATCH --error=/path/to/folder/<some job name>.err
module purge
# Activate the holmesenv virtual environment to use installed packages
# if you need additional packages for your script, install them into /holmesenv/bin/activate
source ~/projects/community/holmesenv/bin/activate
eval "$(conda shell.bash hook)" # Properly initialize Conda
conda activate /projects/community/holmesenv
bash /path/to/your/file/<filename>.sh
#OR
python3 /path/to/your/file/<filename>.py
- then save that whole script as run_NAME.sh (even if the file running is python)
then do this to make both files executable
chmod +x NAME.py chmod +x run_NAME.sh- then run
sbatch run_NAME.sh
Slurm Jobs Tutorial - In Depth
Slurm jobs (sending jobs to be run in the compute cluster) should be used for everything EXCEPT downloads from the internet. Downloads from the internet should be run in login nodes (see below). Non-download jobs should all be packaged and run via slurm in the compute nodes
- Save your script as a scriptname.sh file (or if it’s a python script, scriptname.py)
- Create shell script
- Open a new file in text editor (BBEdit, Textedit, VSCode, etc.)
- paste this code:
#!/bin/bash #SBATCH --partition=p_dz268_1 #SBATCH --job-name=name.sh #SBATCH --cpus-per-task=9 #SBATCH --mem=1G #SBATCH --time=2-00:00:00 #SBATCH --output=/path/batch_jobs/out/name_%A.out #SBATCH --error=/path/batch_jobs/err/name_%A.err module purge # Activate the holmesenv virtual environment to use installed packages eval "$(conda shell.bash hook)" # Properly initialize Conda conda activate /projects/community/holmesenv #change to whatever conda env you need # Run the Python script (or bash) python3 /projects/f_ah1491_1/analysis_tools/script.py- Change time=48:00:00 to however much time you think you’ll need. Max to request is 2 weeks, but the more time you request the longer your slurm job will sit in the queue before running.
- To estimate timing, try downloading 1 subject file and time how long the download takes, then multiply that by number of subjects
- Change
python3 /projects/f_ah1491_1/analysis_tools/script.pyto whatever the script you want to run is - change
/projects/community/holmesenvto whatever conda you need, or keep this as default - change #SBATCH –output and —err paths
- if you have a name like ‘name.out’, that is not changing based on job, it will override each time you run this job, so the err and out file will only be from the most recent run
- if you want to save the err and out file from each run, have the name like name_%A.out
- %A = job ID
- IMPORTANT if running a job array
- %A = job ID
- other ways to name:
- %N = node
- %j = job allocation number
- %a = array index
- change #SBATCH –job-name=name.sh to a name you want to see on the ‘Running jobs’ when you call sacct
- make it short— sacct or watch only allows you to see the first 8 characters of this name
- Doesn’t need to be consistent with anything else
- can also have the % options listed above,
- IMPORTANT if running a job array
Save this file as a run_scriptname.sh file, naming it something relevant to the package + shell
- Make sure both .sh files are in the SAME folder in your home directory, or somewhere in amarel, not on your local computer
- open terminal ($ indicates terminal entry)
- $
cd /home/netID/folder...← replace with wherever your run_scriptname.sh files are saved - $
chmod ugo+rwx filename.extchmod ugo+rwx run_filename.ext - $
chmod ugo+rwx dirname - $
sbatch run_filename.sh
- $
- check in terminal using
sacctto see if your job worked- Make sure state says “Running”
- 2 days a month is maintenance, so jobs will say “failed” during those times. Maintenance calendar: https://oarc.rutgers.edu/amarel-system-status/
Helpful commands
- if anything weird comes up can do
scancel <your netID> sacct -eshows all the variables you could pull up for existing/past jobssacct —state=failed, running, pending, completed
From Cluster User Guide: 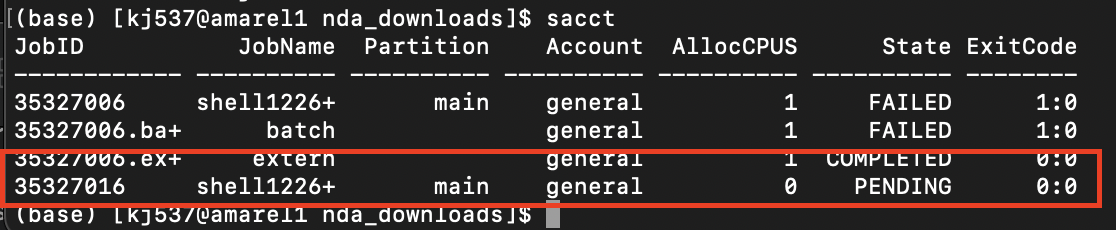
Troubleshooting:
- open error files via:
cd /dir/where error file is/ vi slurm.most.recent.errthe top line will be the reasoning
- check permissions
- check everything is in the right folders
Tips:
- if anything weird comes up can do
scancel <job number> sacct -eshows all the variables you could pull up for existing/past jobs- —state=failed, running, pending, completed
- try it with one subject, see time, multiply by subjects = time estimate
OARC Tutorials
- Job partitions (job submission queues)
- Job scheduler (batch system)
- Current configuration
- Serial job example
- Parallel (multicore MPI) job example
- Interactive job example
- Parallel interactive job example
- Job array example
- Some helpful tips
- Monitoring job status
- Actively running jobs
- Completed or terminated jobs
- Cancelling jobs
- Rutgers Slurm Job / Batch User Guide